Weak Bases and Base Ionization Constants
Topic Description
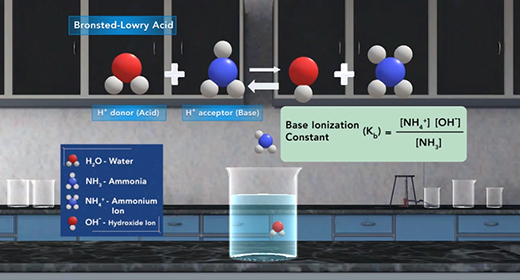
Upon completion of this module, you should be able to explain what is meant by the base ionization constant (Kb) and use Kb values to order bases according to their strength. Bronsted-Lowry defined a base as a proton (hydrogen ion) acceptor and acid as a proton donor. For example, ammonia, NH3, acts as a base (it accepts a proton or H+ ion) when it is mixed with water H2O, which donates a hydrogen ion and serves as Bronsted-Lowry acid.

The topic "Weak Bases and Base Ionization Constants" is available as part of this package. Subscribe this package to get access to this topic.