Corporate Headquarters
475 Metro place South, Suite 120, Dublin, OH 43017, USA,
Direct: +1 614-707-5225
Global Technology Center
SKCL Infinite Towers, A21 & A22, Thiru-vi-ka Ind. Estate, Guindy, Chennai-600032, India,
Direct: +91 (44)-2250-1363
Virtual Reality
in Manufacturing
Virtual Reality (VR) provides innovative tools and experiences that can help envision and build the industry's future. Embracing new technologies is crucial for the manufacturing industry as it works to modernize and address national challenges.
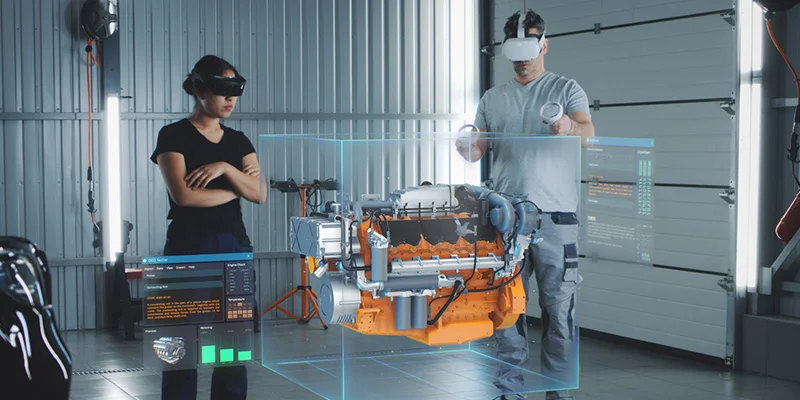

Most Popular Packages for Manufacturing
XR Guru
Heavy Equipment Safety & Operation
Learn and Practice Operating Heavy Equipment in a hands-on VR Training Environment
For 1 user $500.00 - 12 months
View DetailsXR Guru
Aerial Lifts
Aerial Lift Training in an Interactive VR Environment: Personnel, Boom, and Scissor Lifts

For 1 user $500.00 - 12 months
View DetailsXR Guru
Manufacturing Skills and Safety
Learn to navigate high-risk environments in VR: lockout-tagout, harness use, and fall prevention

For 1 user $749.99 - 12 months
View DetailsGW Pro
Industrial Safety Bundle
GW Pro VR offers virtual safety training with hands-on guidance


For 1 user $3,000.00 - 12 months
View DetailsUse Cases
Discover Examples of VR Solutions for Manufacturing

3D Modelling and Design
Virtual Reality (VR) takes the design process to the next level. By creating a realistic digital twin of a proposed manufacturing plant, plans can be rigorously examined at the design stage. Being able to walk around a virtual site means that issues can be flagged and addressed at an earlier stage. This can help to minimize costly and time-consuming alterations further down the line significantly.

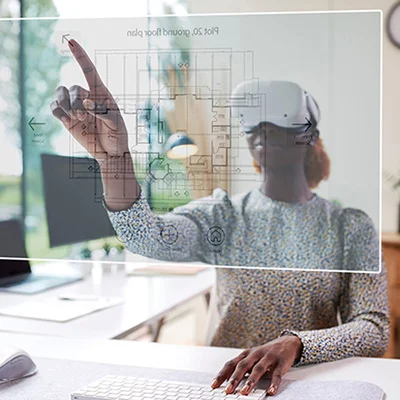
Client Relationship Management
Client relationships can also benefit from Virtual Reality (VR). Creating a virtual completed site before it’s built allows clients to visualize, tour, experience, and scrutinize it from the start of the project. This will help them realize their vision more accurately, as AR and VR helps remove any ambiguities around their expectations and allows adjustments to be made before manufacturing begins.

Training
One thing that all manufacturing projects have in common is that they rely on collaborative work for the completion of interdependent tasks. But often, these relationships are challenged by fragmented working practices. Virtual Reality (VR) can help to improve communications throughout the project’s lifespan, from sharing the finished vision in minute detail to providing site updates to those unable to visit the site regularly.

Maintenance and Inspection
One thing that all manufacturing projects have in common is that they rely on collaborative work for the completion of interdependent tasks. But often, these relationships are challenged by fragmented working practices. Virtual Reality (VR) can help to improve communications throughout the project’s lifespan, from sharing the finished vision in minute detail to providing site updates to those unable to visit the site regularly.
Why Use Virtual Reality (VR) in Manufacturing
Save Time and Costs
Virtual Reality (VR) solutions streamline training by providing real-time guidance and instructions, cutting costs. Engineers can construct full-scale virtual models to visualize equipment in product design, eliminating the need for physical prototypes. Research suggests this approach can reduce training time by up to 75% per person.

Increase Productivity
Forward-thinking manufacturers currently use Virtual Reality (VR) to improve their approach to predictive analytics. VR allows manufacturers to spot a design flaw in just a few minutes. Manufacturers can quickly detect bottlenecks and areas needing improvement by studying the production process in a virtual environment.
Improve Safety
Safety is another area where Virtual Reality (VR) can be successfully applied. By digitally simulating the production processes, it’s possible to identify dangerous maneuvers in advance. The exact procedure can improve consumers’ safety by simulating the actual circumstances in which a product will be used.
Improve Quality
Virtual Reality (VR) greatly enhances manufacturing precision by improving quality assurance processes and goods. 3D visualization enables engineers to view all components and assembly instructions accurately. This facilitates more efficient testing and quality assurance, ensuring proper installation of each product part by technicians.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is VR used in manufacturing?
Virtual Reality (VR), when used in the manufacturing industry, can help with many issues, such as increasing productivity, reducing training costs, and decreasing the time required to take new products to market. Manufacturing organizations can streamline their processes by transferring risky and challenging procedures to VR, which may help reduce costs. Employee safety is essential when it comes to working in manufacturing. Virtual reality allows management to get a glimpse of specific issues of concern, make changes, and provide a safer work environment without the risk of employee injury in the process. Manufacturers and product designers often face various problems in designing prototypes and the manufacturing process itself. Virtual Reality meets each manufacturer's requirements to lower costs, improve quality, and move production processes to a new level.
Why is Virtual Reality important for manufacturing?
Virtual Reality, when used in the manufacturing industry, can help with a wide range of issues such as increasing productivity, reducing training costs, and increasing the availability of new products to market.
How can VR improve manufacturing instructions?
VR is widely used for employee instruction and education as it can simulate every possible process and environment. Manufacturing organizations can use VR to create solutions that guide assembly line workers through every intricate detail of the production process in real-time. A worker gets virtual instructions projected into his VR headset as he proceeds with his work. This helps organizations save weeks or even months of lengthy training and accounts for eliminating the notorious human factor and avoiding mistakes. By providing guidance and instructions in real-time, VR solutions help reduce training and coaching expenses; they also help organizations reallocate resources by letting their most experienced workers focus on areas that need expertise and attention.
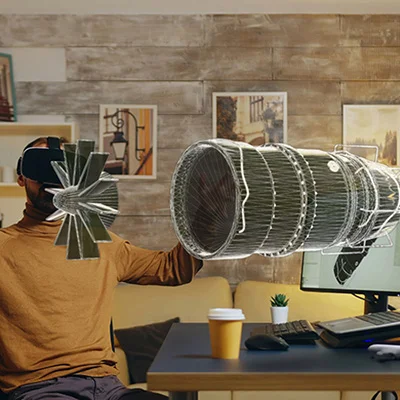
How Virtual Reality is impacting manufacturing design and engineering?
The prototyping step is usually always a part of the design process in manufacturing. The new product prototype is ready to be examined, tried, and tested before being determined to be ready for production or in need of some adjustment. The prototype could be expensive, especially if the product is a complicated piece of machinery. Additionally, the cost of the prototype can increase if it needs more refinement. With Virtual Reality, teams of engineers and designers don’t have limits in creating prototypes, as everything can be easily corrected and fixed before the exact physical prototype is even built. VR prototyping can also be a breakthrough in a designer’s creativity. They do not have any limits while inventing new solutions and designs. Thanks to VR, designers and engineers can explore options that would have been cost- or time-prohibitive in the past. Shifting the prototype to virtual reality can offer immense benefits. The overall expenses can be less than creating a line of physical prototypes, even after accounting for the cost of developing the Virtual Reality app.
What are the pros and cons of VR in manufacturing?
'Virtual Reality (VR) provides several benefits to manufacturing organizations, such as improving safety by helping to detect and eliminate threats, ensuring better quality, and reducing costs by eliminating the costly trial and error phase and reducing training and coaching expenses. However, implementing VR in industrial manufacturing will require time and investment. It also involves meeting challenges like indicating areas for its implementation, integration with legacy equipment, support on the employee level, etc. The best practices for enterprise-scale VR implementation involve launching a pilot project and moving on according to its outcome.
What is the difference between VR and VR in manufacturing?
Virtual Reality (VR) is an umbrella term for Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR). Both VR and VR provide several benefits to manufacturing organizations, such as (1) improving safety by helping to detect and eliminate threats, instructing employees, and thus reducing the number of onsite accidents; (2) bringing increased precision to every aspect of the industrial manufacturing process, ensuring a better quality of manufactured goods; and (3) reducing costs by eliminating the costly trial and error phase and providing guidance and instructions in real-time - helping to reduce training and coaching expenses.
What are the advantages of Virtual Reality in the manufacturing industry?
In manufacturing, the transformative potential of Virtual Reality (VR) is inherently tied to the demand for continuous production and non-disruptive performance, every second of downtime spells revenue loss. Today, Virtual Reality is helping manufacturers reduce expenses, increase security/safety, take designers’ and engineers’ work to a new level, improve quality, eliminate disruptions and downtime, and make training more efficient. Specifically, VR is creating positive disturbance in manufacturing for many operational processes, from design and prototyping to the final production and assembly.
How VR is used for inventory management in manufacturing?
VR technology can help eliminate confusion and make the inventory management process quick and precise. A warehouse worker wearing a VR headset gets instructions about the exact location of a particular item and is guided to the very aisle and shelf where it is stored. No more guesswork and getting lost amidst the similarly looking shelves – anyone who has ever been inside an industrial warehouse can understand the value of this solution.
How VR is used for additional safety in manufacturing?
Safety is essential when it comes to working in manufacturing. Virtual Reality allows management to get a glimpse of specific issues of concern, make changes, and provide a safer work environment without the risk of employee injury in the process.
How VR is used for maintanence in manufacturing?
Today, many machines are too complicated for typical production workers to inspect. Companies frequently need to invite experts from the company that produced the equipment for any routine or emergency examination. Such inspection visits are typically expensive, and since inspectors’ schedules are sometimes occupied for weeks, it could be challenging to schedule an appointment when a machine unexpectedly breaks down. Virtual Reality (VR) allows an expert to inspect equipment remotely. Inspections and remote maintenance can be completed in Virtual Reality quickly and with fewer interruptions to the production cycle when travel time and costs are no longer a factor.
How VR is used for business exhibition in manufacturing?
Manufacturers who present their products at trade shows and exhibits typically struggle to set up shop at the venue, especially heavy machinery manufacturers. The job is intricate and multifaceted. The maker must consider the machine’s shipping, connection, and use at the show. A machine may require a large amount of space and weigh several tons, which results in additional expenses for the renting of the display area as well as for loading and unloading. Finding a piece of equipment to show may be another issue that equipment manufacturers find problematic, for heavy equipment is typically produced in response to requests and is not always readily available. Virtual Reality can help resolve these issues. By creating a VR app showcasing your equipment, you can downsize your exhibition space, for you can display machinery and equipment of any size and complexity in Virtual Reality. Additionally, by inviting exhibition visitors to your VR room, you may demonstrate the technology in action without putting guests in danger.
Will accidents decrease while using VR in manufacturing site?
The manufacturing sector has a higher risk of accidents than others. Numerous reasons can lead to accidents at work. Among them are falling objects in the warehouse, equipment failure, high noise, etc. VR product design and manufacturing increase the predictability of production processes, consequently increasing security and safety. Virtual Reality technology helps detect and eliminate threats so that the number of onsite accidents can be reduced. It helps identify potentially dangerous situations so they can be effectively addressed and eliminated.
What are the key Virtual Reality in manufacturing industry drivers?
Numerous studies point to a reduction in workers available for manufacturing jobs and a growing skill gap. In the next decade, 2 million of the available 3.5 million manufacturing jobs in the U.S. will go unfilled because of a lack of skilled workers, according to a study by Deloitte. VR can speed up the onboarding of new workers and improve worker productivity by offering more immersive on-the-job training. In manufacturing, the transformative potential of Virtual Reality (VR) is inherently tied to the demand for continuous production and non-disruptive performance, every second of downtime spells revenue loss. Today, Virtual Reality is helping manufacturers to lower costs, increase productivity, and improve quality.
How VR applications help in safety and training in manufacturing sectors?
Virtual Reality technology helps detect and eliminate threats, instruct employees and thus reduce the number of onsite accidents. VR is widely used for employee instruction and education as it can simulate every possible process and environment, including guiding assembly line workers through every intricate detail of the production process in real time. This helps organizations save weeks or even months of lengthy training and accounts for eliminating the notorious human factor and avoiding mistakes.
How will Virtual Reality impact manufacturing?
In manufacturing, the transformative potential of Virtual Reality (VR) is inherently tied to the demand for continuous production and non-disruptive performance, every second of downtime spells revenue loss. Today, Virtual Reality is helping manufacturers reduce expenses, increase security/safety, take designers’ and engineers’ work to a new level, improve quality, eliminate disruptions and downtime, and make training more efficient. Specifically, VR creates a positive disturbance in manufacturing for many operational processes, from design and prototyping to the final production and assembly.
How can Virtual Reality make manufacturing workplace safety safer?
Although the overall safety for manufacturing workers has improved over the years, just one injury or fatality is too many. Virtual Reality is changing manufacturing by providing additional safety. The use of virtual reality allows plant managers to simulate assembly line configurations and the processes involved in the production, which will enable them to identify situations that may be potentially dangerous. Virtual Reality may also be used as a way for employees to be immersed in a workstation to capture the employee’s task proficiency, movement, and feasibility, ultimately eliminating the risk of potential injuries and fatalities. In addition, training is frequently challenging to plan because students lack practical knowledge, which increases their risk of harm. Virtual Reality exhibits its exceptional capacity to immerse trainees in a realistic setting while eliminating the chance of injury. What are the benefits of VR in manufacturing?
In manufacturing, the transformative potential of Virtual Reality (VR) is inherently tied to the demand for continuous production and non-disruptive performance, every second of downtime spells revenue loss. Today, Virtual Reality is helping manufacturers reduce expenses, increase security/safety, take designers’ and engineers’ work to a new level, improve quality, eliminate disruptions and downtime, and make training more efficient. Specifically, VR creates a positive disturbance in manufacturing for many operational processes, from design and prototyping to the final production and assembly.
Is Virtual Reality the future of manufacturing safety training?
A fantastic way to use Virtual Reality in manufacturing is for safety training. In manufacturing, it is crucial that every employee gets adequately trained on safety. Otherwise, they are not able to safely operate equipment and manufacture products. Unfortunately, such training often requires arranging training courses at different sites because many manufacturing organizations have multiple manufacturing locations. In addition, training is frequently challenging to plan because students lack practical knowledge, which increases their risk of harm. Thanks to VR, safety training can be less expensive, and the quality of the training is greater than regular on-site training or onboarding. Learning new things and going through whole processes is more approachable and easier to follow for participants. In addition, virtual reality exhibits its exceptional capacity to immerse the trainees in a realistic setting while eliminating the chance of injury.
Is Virtual Reality the future of the manufacturing industry?
Manufacturers and product designers often face various problems designing prototypes and manufacturing processes. Today, Virtual Reality is helping manufacturers to lower costs, improve quality, and move production processes to new levels. Will VR be the future of manufacturing?
It’s still too early to know. However, one thing is for sure, Virtual Reality in manufacturing can no longer be described as all hype.
Can Virtual Reality improve manufacturing design intents?
Forward-thinking manufacturers currently use virtual Reality to improve their approach to predictive analytics. While finding flaws in a product design could take weeks of analyzing data, interacting with the product digitally allows you to spot a design flaw in just a few minutes. VR also eliminates the need to build actual full-scale models, which is very convenient in sectors such as aerospace manufacturing, where prototyping can be costly.
Why should I opt VR for manufacturing?
In manufacturing, the transformative potential of Virtual Reality (VR) is inherently tied to the demand for continuous production and non-disruptive performance, every second of downtime spells revenue loss. Today, Virtual Reality is helping manufacturers to lower costs, increase productivity, and improve quality.
How Virtual Reality is changing the manufacturing industry?
While Virtual Reality technology has come to be associated chiefly with gaming and infotainment, it’s gradually finding application in various industries. Specifically, VR is creating positive disruption in manufacturing for many operational processes, from design and prototyping to the final production and assembly.
How VR is set to change the manufacturing industry?
In manufacturing, the transformative potential of Virtual Reality technology is inherently tied to the demand for continuous production and non-disruptive performance; every second of downtime means revenue loss. With VR's potential to create a virtual simulation of just about every facet of the manufacturing process, its use in manufacturing is currently creating positive disruption for a vast number of operational processes - resulting in improved security and workplace safety, a better quality of manufactured goods, increased productivity, and a saving of time and money.
Is VR the future of the manufacturing industry?
Manufacturers and product designers often face various problems designing prototypes and manufacturing processes. Today, Virtual Reality (VR) is helping manufacturers to lower costs, improve quality, and move production processes to new levels. Will VR be the future of manufacturing?
It’s still too early to know. However, one thing is sure: Virtual Reality in manufacturing can no longer be described as all hype.
What is Virtual Reality (VR) in manufacturing?
While Virtual Reality technology (an umbrella term for AR/VR) has become associated primarily with gaming and infotainment, it’s gradually finding application in many industries. Specifically, in manufacturing, VR is creating positive disruption for many operational processes: from design and prototyping to the final production and assembly. Why do I prefer VR manufacturing over traditional manufacturing?
Manufacturers and product designers often face various problems designing prototypes and manufacturing processes. Today, Virtual Reality (VR) is helping manufacturers to lower costs, improve quality, and move production processes to new levels.
How is VR being used for manufacturing in the industry?
Some of the most prominent use cases for Virtual Reality in manufacturing are: (1) improving the design and prototyping process, (2) making the inventory management process quick and precise, (3) preventing accidents and disruptions by identifying and evading the hazards and disruption risks associated with the use of an assembly line, and (4) providing real-time employee instruction and education that helps organizations save weeks or even months of lengthy training and accounts for eliminating the notorious human factor and avoiding mistakes.
How beneficial it is to embrace VR for manufacturing?
A few of the primary benefits provided by Virtual Reality in manufacturing are: (1) improving safety by helping to detect and eliminate threats, instructing employees, and thus reducing the number of onsite accidents; (2) bringing increased precision to every aspect of the industrial manufacturing process, ensuring a better quality of manufactured goods; and (3) reducing costs by eliminating the costly trial and error phase and providing guidance and instructions in real-time - helping to reduce training and coaching expenses.
Why should I opt VR for manufacturing?
In manufacturing, the transformative potential of Virtual Reality technology (an umbrella term for AR/VR) is inherently tied to the demand for continuous production and non-disruptive performance; every second of downtime means revenue loss. With VR's potential to create a virtual simulation of just about every facet of the manufacturing process, its use in manufacturing is currently creating positive disruption for a vast number of operational processes - resulting in improved workplace safety and the quality of manufactured goods, increased productivity, and a reduction in expenses.
How Virtual Reality is changing the manufacturing industry?
In manufacturing, the transformative potential of Virtual Reality (VR) is inherently tied to the demand for continuous production and non-disruptive performance, every second of downtime spells revenue loss. Today, Virtual Reality is helping manufacturers reduce expenses, increase security/safety, take designers’ and engineers’ work to a new level, improve quality, eliminate disruptions and downtime, and make training more efficient. Specifically, VR is creating a positive disturbance in manufacturing for many operational processes, from design and prototyping to the final production and assembly.
Is Virtual Reality the future of manufacturing safety training?
Virtual Reality (VR) can be used as a way for employees to be immersed in a workstation to capture the employee’s task proficiency, movement, and feasibility, ultimately eliminating the risk of potential injuries and fatalities. In addition, training is frequently challenging to plan because students lack practical knowledge, which increases their risk of harm. Virtual Reality exhibits its exceptional capacity to immerse trainees in a realistic setting while eliminating the chance of injury.
Can Virtual Reality improve manufacturing design intents?
Forward-thinking manufacturers currently use Virtual Reality (VR) to improve their approach to predictive analytics. While finding flaws in a product design could take weeks of analyzing data, interacting with the product digitally allows you to spot a design flaw in just a few minutes. VR also eliminates the need to build actual full-scale models, which is very convenient in sectors such as aerospace manufacturing, where prototyping can be costly.
What are the benefits of VR in manufacturing?
A few of the primary benefits provided by Virtual Reality in manufacturing are: (1) improving safety by helping to detect and eliminate threats, instructing employees, and thus reducing the number of onsite accidents; (2) bringing increased precision to every aspect of the industrial manufacturing process, ensuring a better quality of manufactured goods; and (3) reducing costs by eliminating the costly trial and error phase and providing guidance and instructions in real-time - helping to reduce training and coaching expenses.
How VR applications are helpful in safety and training in manufacturing sectors?
Virtual Reality technology helps detect and eliminate threats, instruct employees and thus reduce the number of onsite accidents. VR is widely used for employee instruction and education as it can simulate every possible process and environment, including guiding assembly line workers through every intricate detail of the production process in real-time. This helps organizations save weeks or even months of lengthy training and accounts for eliminating the notorious human factor and avoiding mistakes.
Why integrate VR into manufacturing?
Virtual Reality (VR), when used in the manufacturing industry, can help with a wide range of issues, such as increasing productivity, reducing training costs, and increasing the availability of new products to market.
How VR is transforming manufacturing?
In manufacturing, the transformative potential of Virtual reality technology (an umbrella term for AR/VR) is inherently tied to the demand for continuous production and non-disruptive performance; every second of downtime means revenue loss. With VR's potential to create a virtual simulation of just about every facet of the manufacturing process, its use in manufacturing is currently creating positive disruption for a vast number of operational processes - resulting in improved security and workplace safety, a better quality of manufactured goods, increased productivity, and a saving of time and money.



