The Third Law of Thermodynamics
Topic Description
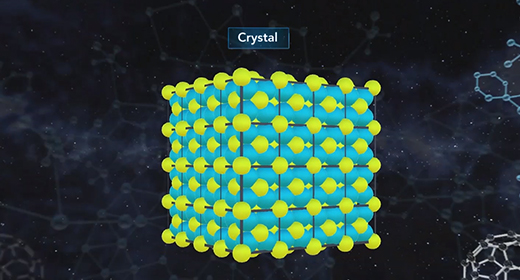
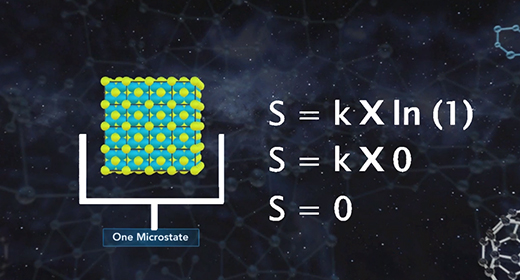
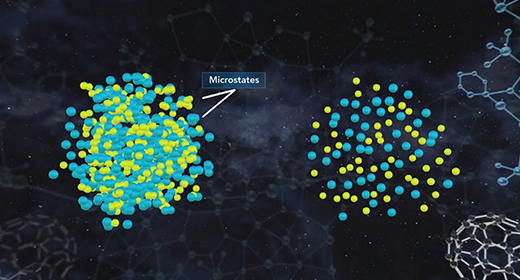
Upon completion of this module, you should be able to know the relationship between entropy and microstates and know the value of entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero. According to the third law of thermodynamics, the entropy of a perfect crystal at zero kelvin, known as absolute zero, is equal to zero. In a perfect crystal, the spatial distribution of its constituent particles is constant throughout. Entropy quantifies the disorder of a system increases as the number of microstates increases. As the temperature of a system approaches absolute zero, the number of microstates approaches one. Entropy, S, is equal to the product of the Boltzmann constant, k, and the natural log of the number of microstates, W.

The topic "The Third Law of Thermodynamics" is available as part of this package. Subscribe this package to get access to this topic.