The Concept of Equilibrium and the Equilibrium Constant
Topic Description
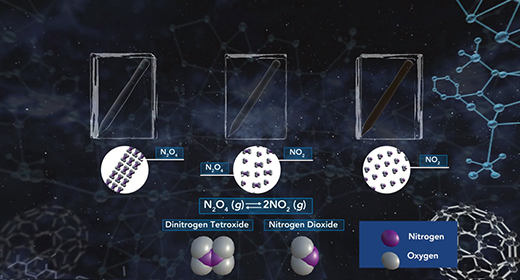
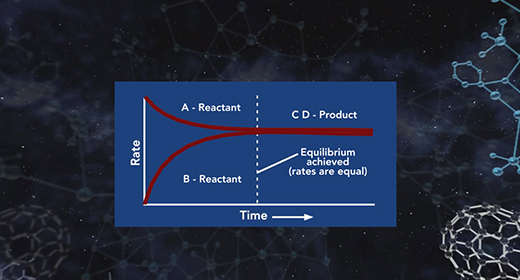
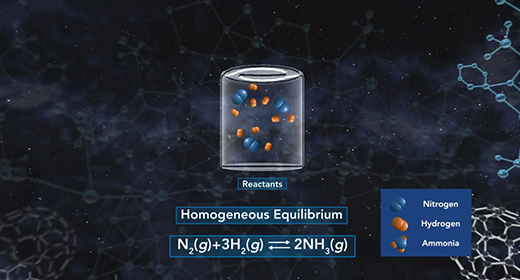
Upon completion of this module, you should be able to explain what is meant by chemical equilibrium, explain how the equilibrium constant is determined, understand what the magnitude of the chemical equilibrium constant means and Explain the difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibria. Equilibrium is a state that a reaction achieves when no new observable changes occur. A chemical reaction reaches its equilibrium when the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal, and both reactant and product concentrations remain constant.

The topic "The Concept of Equilibrium and the Equilibrium Constant" is available as part of this package. Subscribe this package to get access to this topic.