The Common Ion Effect
Topic Description
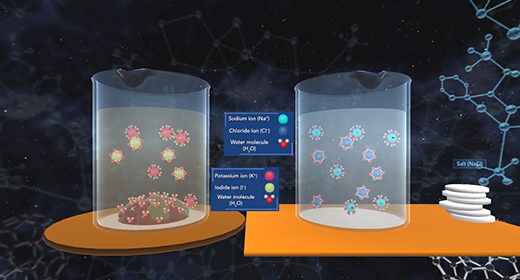
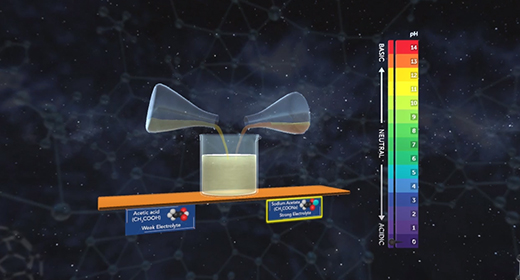
Upon completion of this module, you should be able to explain the common ion effect and understand the effect of a common ion on the dissociation of a weak acid and a weak base. The degree to which a weak electrolyte will dissolve in water is reduced by the presence of a strong electrolyte that has an ion in common with the weak electrolyte. This is the common ion effect. A combination of salts in an aqueous solution will all ionize according to the solubility product for each salt which is equilibrium constants. If the salts share a common cation or anion, both contribute to the concentration of the common ion and need to be included in concentration calculations. As one salt dissolves, it affects how well the other salt can dissolve, essentially making it less soluble.

The topic "The Common Ion Effect" is available as part of this package. Subscribe this package to get access to this topic.