Reaction Mechanisms
Topic Description
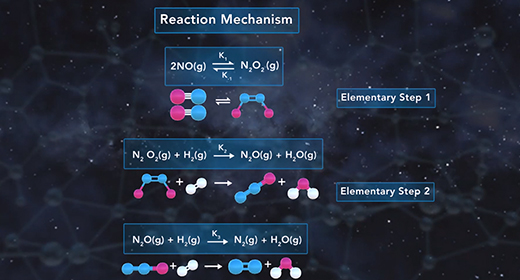
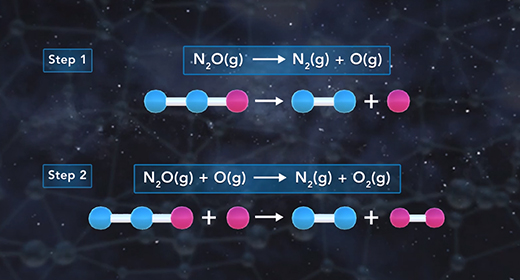
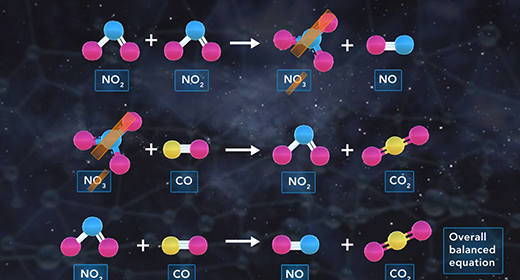
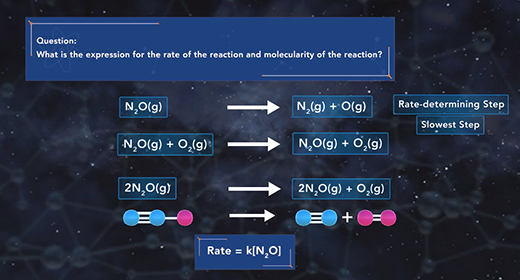
Upon completion of this module, you should be able to explain what is meant by a reaction mechanism, define intermediate, describe the effect of the rate-determining step on the rate of a chemical reaction, and determine the molecularity of a reaction. The reaction mechanism describes the overall progress of a chemical reaction at the molecular level using a series of simple elementary steps. For example, the reaction shown has three steps. The second step is slow, and the third one is fast. The reaction mechanism cares about the sequence of elementary steps that leads to product formation. The intermediate of a reaction mechanism is a substance that appears in the reaction steps but not in the overall balanced equation because an intermediate is a product in one elementary step but then gets consumed as a reactant in a later elementary step.

The topic "Reaction Mechanisms" is available as part of this package. Subscribe this package to get access to this topic.