Hybridization of Single Double and Triple Bonds
Topic Description
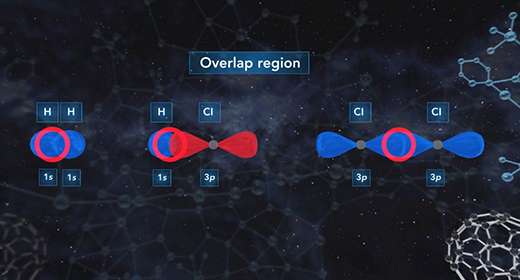
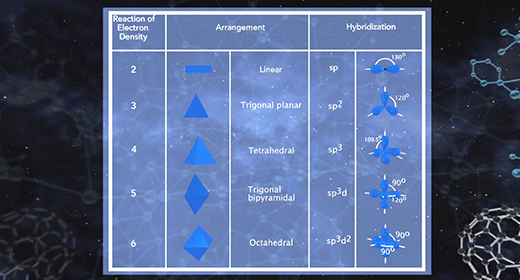
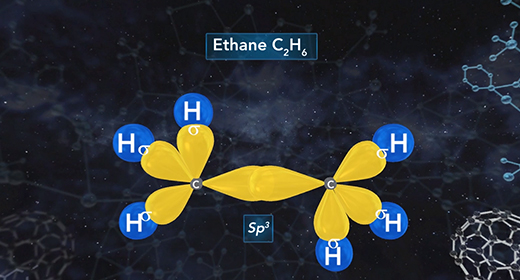
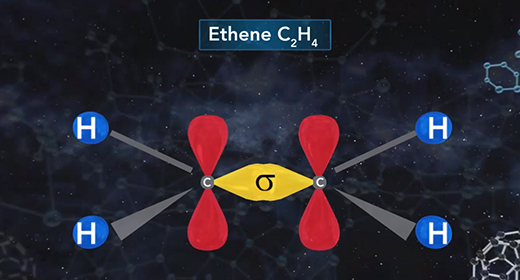
Upon completion of this module, you should be able to describe the hybridization in molecules containing a single bond, describe the hybridization in molecules containing a double bond, and describe the hybridization in molecules containing a triple bond. Hybridization is the mixing of two or more atomic orbitals to form a new set of hybrid orbitals. When two or more atomic orbitals combine, a hybrid orbital with a different shape can form. The total number of hybrid orbitals is equal to the number of pure atomic orbitals used in the hybridization process. The overlap of hybrid orbitals of different atoms forms covalent bonds between those atoms. The shape of molecules with hybridized orbitals can be linear (sp), trigonal planar (sp2), tetrahedral (sp3), trigonal bipyramidal (sp3d), octahedral (sp3d2).

The topic "Hybridization of Single Double and Triple Bonds" is available as part of this package. Subscribe this package to get access to this topic.