Acid Ionization Constants
Topic Description
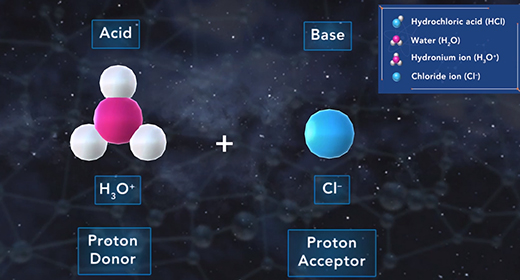
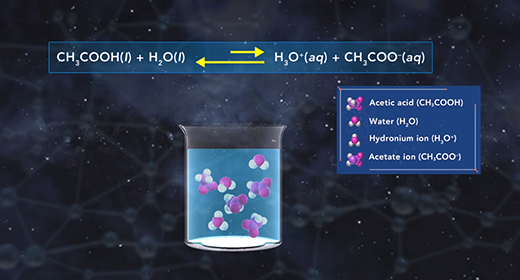
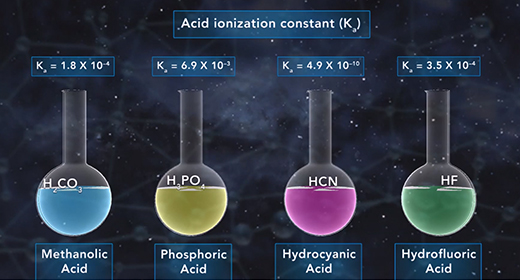
Upon completion of this module, you should be able to explain how to determine the acid ionization constant (Ka) and order acids according to their strength based on their (Ka) value. Bronsted-Lowry defined an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor. For example, acetic acid acts like acid if it donates a proton when it reacts with water, which accepts the proton and acts as a Bronsted-Lowry base. When weak acids, such as acetic acid, dissociate in water, only a small fraction of the weak acid molecules dissociate into ions.

The topic "Acid Ionization Constants" is available as part of this package. Subscribe this package to get access to this topic.